A marker’s felt nib proves to be an excellent medical sampler

Researchers from MIPT, Skoltech and IMPB RAS have developed a compact sampling probe that facilitates biological sample collection for ambient ionization mass spectrometry analysis. This kind of sampler can be effectively used even on board a space station. The findings were published in Acta Astronautica.
Most of us have had a nasopharyngeal swab taken with a cotton-tipped stick or, in scientific terms, a sampler. Biological sampling devices used nowadays are highly sensitive to storage conditions and require a low temperature or high humidity environment depending on the test, while samples have a short storage life of only a few hours, which strongly limits in-field sample collection both on Earth and in space.
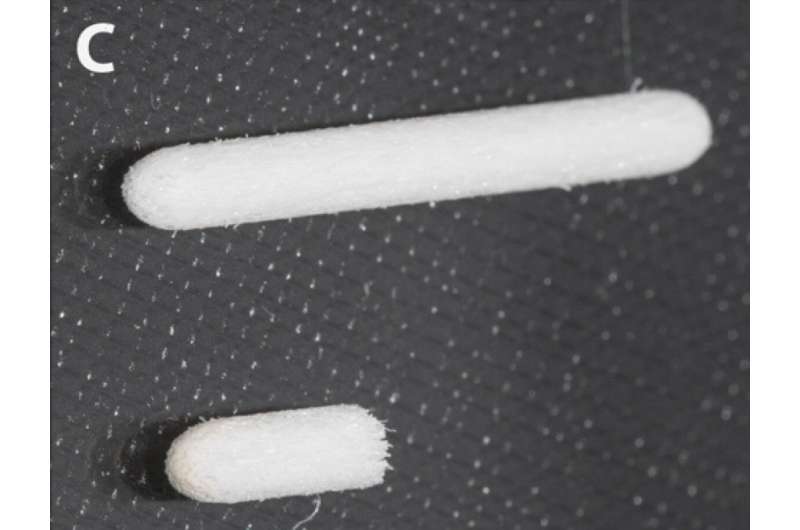
The team decided to look at porous materials in search of a suitable replacement for existing probes and discovered that felt used in soft-tip pens can be a handy and effective material for collecting biological fluids from the skin, mucosa, wounds, and lesions. This lightweight material does not require refrigeration or constant storage temperatures, pressure and humidity, while ensuring longer sample storage life.
“For the probe to be as versatile as possible, it should be lightweight, small, easy to handle and ready to be connected to the mass spectrometer in order to pick signals from the collected molecules right away. While performing the tests, we came to realize that a rigid spherical sampler made from porous fibrous polypropylene is best suited for the task, because it readily absorbs various compounds, while retaining its initial shape during sampling, transportation, and storage. This increases both the electrospray ionization stability and sensitivity, and, therefore, the test accuracy,” Igor Popov, study lead and head of the MIPT Laboratory of Molecular Medical Diagnostics, explains.
The team’s rod-shaped sampler made from clean compressed low-density polypropylene fibers makes sample storage much easier: dried biological samples can be stored at room temperature and are not affected by abrupt changes in pressure and temperature. The rigidity and sphericity of the probe enables taking swabs without using any additional tools, while increasing the test sensitivity and expanding the range of analyzed molecules, primarily small molecules, such as drugs and metabolites, which are of particular interest for drug research in space. In addition, the polypropylene sampler can be used for mass spectrometry without prior preparation, which makes biomaterial analysis much simpler.
Mass spectrometry has recently evolved into one of the key tools for biomedical tests. Its further advancement could provide a wealth of benefits for biomarker screening, intraoperative monitoring, toxicology, emergency medical care, forensics, food industries and farming, where simple sampling techniques without additional pre-treatment are of vital importance. All this underscores the high relevance of the study.
Source: Read Full Article