Blood plasma protein fibrinogen interacts directly with nerve cells to cause brain inflammation
Neuroinflammatory diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease and traumatic brain injury, have been linked to deposits of a tough protein known as fibrin, derived from the blood clotting factor fibrinogen. These mesh-like fibrin deposits occur outside blood vessels in the brain, contributing to the death of certain central nervous system cells (neurons) that eventually leads to impaired memory.
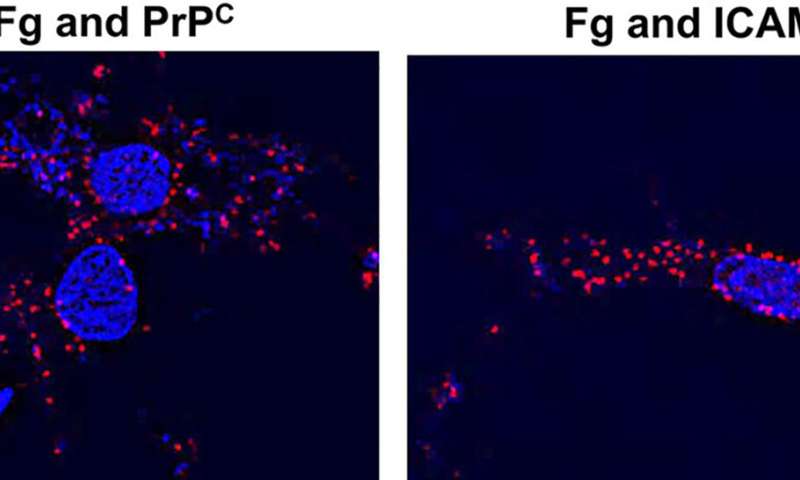
Now for the first time, a team at the University of South Florida Health (USF Health) Morsani College of Medicine, reports that before soluble fibrinogen is converted into insoluble fibrin molecules that can adversely accumulate, it can connect directly with neurons and cause a damaging inflammatory reaction. The researchers further discovered that fibrinogen specifically binds to two fibrinogen receptors on the surface of neurons: Cellular prion protein (PrPC) and intracellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1).
Their preclinical study was published Sept. 18 in a special issue entitled “Prions and Prion-Like Mechanisms in Disease and Biological Function” in MDPI-Biomolecules.
The findings have implications for identifying targeted therapies to help prevent or stop neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease, traumatic brain injury, or other chronic neuroinflammatory diseases associated with abnormal vascular permeability (leakage) in the brain.
“Fibrinogen is one of the overlooked culprits involved in the processes of neurodegeneration and resulting memory loss,” said principal investigator David Lominadze, Ph.D., a USF Health professor of surgery, and molecular pharmacology and physiology. “Our study shows that fibrinogen is not only a marker (biological indicator) of inflammation but can be a cause of inflammation in the brain.”
Fibrinogen is a protein naturally produced in the liver and travels throughout the bloodstream to other organs and tissues. Outside of blood vessels, fibrinogen is converted by the enzyme thrombin into fibrin during blood clot formation, playing a key role in wound healing.
Dr. Lominadze’s laboratory focuses on understanding molecular changes affecting circulation of blood in the body’s smallest blood vessels—including how microvascular changes induced by inflammation may damage cognition, in particular short-term memory.
Dr. Lominadze and others have shown that inflammatory disease is associated with a higher concentration of fibrinogen in the blood, increased generation of potentially damaging free radicals, neuronal cell activation and microvascular permeability. In previous studies using their mouse model for mild-to-moderate traumatic brain injury, Dr. Lominadze’s group reported that fibrinogen after crossing the vascular wall accumulated in spaces between the microvessels and astrocytes (another brain cell type connecting vessels and neurons) and activated the astrocytes. This activation coincided with increased neurodegeneration and reduced short-term memory.
In this latest study, the USF Health researchers tested whether fibrinogen, beside interacting with astrocytes, could connect directly with neurons—nerve cells critical for carrying information throughout the human body and coordinating all necessary functions of life.
They treated healthy mouse brain neurons grown in a petri dish with fibrinogen. Fibrinogen increased the death of these neurons, a process that was not influenced by the presence or absence of a thrombin inhibitor preventing the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin. The finding suggests that soluble fibrinogen—and at later stages, fibrin—can have similar toxic effects on neurons.
Furthermore, blocking the function of PrPC and ICAM-1 fibrinogen receptors on the surface of neurons (essentially stopping fibrinogen from binding tightly to these receptors) reduced inflammatory reactions resulting in neurodegeneration.
“The study revealed that an interaction between fibrinogen and neurons induced an increase in the expression of proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 (IL-6), enhanced oxidative damage, and neuronal death, in part due to its direct association (contact) with neuronal PrPC and ICAM-1,” the study authors wrote.
Source: Read Full Article