Study offers hope of new treatment for progeria syndrome in children
Researchers from Karolinska Institutet and Gothenburg University have investigated a potential new drug target for the rare genetic disorder Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome that causes accelerated aging in children. The findings in mice are published in the scientific journal eLife and may aid in the development of more effective treatments for this fatal condition.
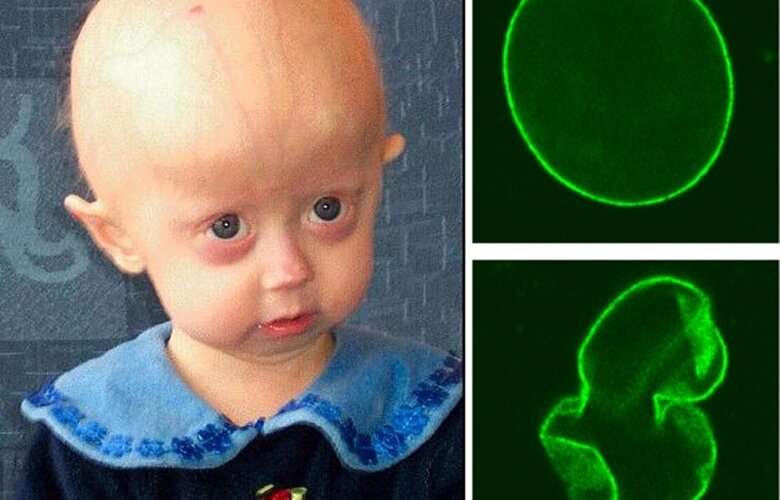
Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome, HGPS, is a progressive genetic disorder that causes rapid and premature aging in children. The disease is caused by progerin, a mutant protein that accumulates between the membranes that surround the cell nucleus, leading to damage that makes cells slow down their growth and die prematurely.
The new findings in mice show that blocking a protein called ICMT, which is involved in modifying the structure of progerin, can improve the condition of affected cells without reducing cell division and growth.
Effect in mice and cells
The researchers inactivated the ICMT gene in mice with HGPS and observed how it affected their health. They found that the mice which lacked ICMT survived significantly longer, and had higher body weights, compared to unmodified mice with progeria. They also had larger skeletal muscle fibres, and the muscle cells around their aorta resembled those of healthy mice. This result is particularly important as cardiovascular problems are the main cause of mortality in children with HGPS.
The researchers also treated human HGPS cells and HGPS-mimicking cells from mice with a synthetic chemical called C75 that strongly inhibited the ICMT protein. This treatment delayed the deterioration of the cells and stimulated cell division and growth. When applied to healthy human cells and mouse cells that lacked the ICMT protein, C75 had no significant unintended effects, suggesting that it has good specificity for HGPS.
Important step toward new drug target
Source: Read Full Article


