New virus variant emerges in Africa, stokes worldwide fears
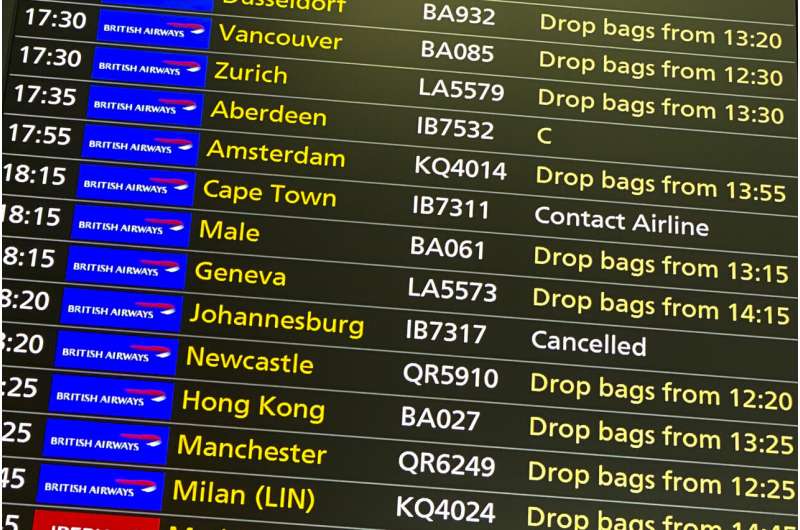
The discovery of a new coronavirus variant sent a chill through much of the world Friday as nations raced to halt air travel, markets plunged and scientists held emergency meetings to weigh the exact risks, which were largely unknown.
Medical experts, including the World Health Organization, warned against any overreaction before the variant that originated in southern Africa was better understood. But a jittery world feared the worst nearly two years after COVID-19 emerged and triggered a pandemic that has killed more than 5 million people around the globe.
British Health Secretary Sajid Javid told lawmakers that the new version may be more transmissible than the delta variant and render vaccines less effective.
“We must move quickly and at the earliest possible moment,” Javid said.
Some nations moved to stop air travel from southern Africa, and stocks plunged in Asia, Europe and the United States. The Dow Jones Industrial Average dropped 800 points at the start of trading. The price of oil plunged 7%.
“The last thing we need is to bring in a new variant that will cause even more problems,” German Health Minister Jens Spahn said amid a massive spike in cases in the 27-nation European Union, which recommended a ban on flights from southern African nations.
EU Commission President Ursula von der Leyen said flights “should be suspended until we have a clear understanding about the danger posed by this new variant, and travelers returning from this region should respect strict quarantine rules.”
She insisted on extreme caution, warning that “mutations could lead to the emergence and spread of even more concerning variants of the virus that could spread worldwide within a few months.
Belgium became the first European Union country to announce a case of the variant. It involved a person who came from abroad.
“It’s a suspicious variant. We don’t know if it’s a very dangerous variant,” Health Minister Frank Vandenbroucke said.
Israel, one of the world’s most vaccinated countries, announced Friday that it also detected the country’s first case of the new variant in a traveler who returned from Malawi. The traveler and two other suspected cases were placed in isolation. Israel said all three were vaccinated, but officials were looking into the travelers’ exact vaccination status.

The new variant immediately stoked fears of more pandemic-related economic turmoil.
“Investors are likely to shoot first and ask questions later until more is known,” said Jeffrey Halley of foreign exchange broker Oanda.
Oil prices plunged, with U.S. crude off 6.7% at $73.22 per barrel and the international Brent benchmark off 5.6% at $77.64, both unusually large moves for a single day. The pandemic caused oil prices to plunge during the initial outbreak of the pandemic in 2020 because travel restrictions reduced demand for fuel.
Airlines shares were hammered, with Lufthansa off 12.4%, IAG, parent of British Airways and Iberia, off 14.4%, Air France-KLM down 8.9% and easyJet falling 10.9%.
Speaking before the EU announcement, Dr. Michael Ryan, the head of emergencies at the WHO, warned against “knee-jerk responses.”

“We’ve seen in the past, the minute there’s any kind of mention of any kind of variation and everyone is closing borders and restricting travel. It’s really important that we remain open and stay focused,” Ryan said.
The Africa Centers for Disease Control and Prevention agreed and strongly discouraged any travel bans on countries that reported the new variant. In a statement, it said past pandemic experience has shown that such travel bans have “not yielded a meaningful outcome.”
The U.K. banned flights from South Africa and five other southern African countries effective at noon on Friday and announced that anyone who had recently arrived from those countries would be asked to take a coronavirus test.
Germany said its flight ban could be enacted as soon as Friday night. Spahn said flights returning from South Africa will only be able to transport German citizens home, and travelers will need to go into quarantine for 14 days whether they are vaccinated or not.

Germany has seen record daily case numbers in recent days and on Thursday surpassed 100,000 deaths from COVID-19.
Italy’s health ministry also announced measures to ban entry for anyone who has been in seven southern African nations—South Africa, Lesotho, Botswana, Zimbabwe, Mozambique, Namibia and Eswatini—in the past 14 days due. The Netherlands and the Czech Republic planned similar measures.
The Japanese government announced that Japanese nationals traveling from Eswatini, Zimbabwe, Namibia, Botswana, South Africa and Lesotho will have to quarantine at government-dedicated accommodations for 10 days and take COVID-19 tests on the third, sixth and tenth days. Japan has not yet opened up to foreign nationals.
The South African government said that the U.K.’s decision to temporarily ban South Africans from entering “seems to have been rushed,” citing the fact that the WHO has yet to recommend next steps.



The coronavirus evolves as it spreads and many new variants, including those with potentially risky mutations, often die out. Scientists monitor for possible changes that could be more transmissible or deadlier, but sorting out the exact dangers of new variants takes time.
The WHO’s technical working group is to meet Friday to assess the new variant—currently identified as B.1.1.529—and may decide whether to give it a name from the Greek alphabet. It says coronavirus infections jumped 11% in Europe in the past week, the only region in the world where COVID-19 continues to rise.
Source: Read Full Article


