Macrophages play key role in lung damage during COVID-19
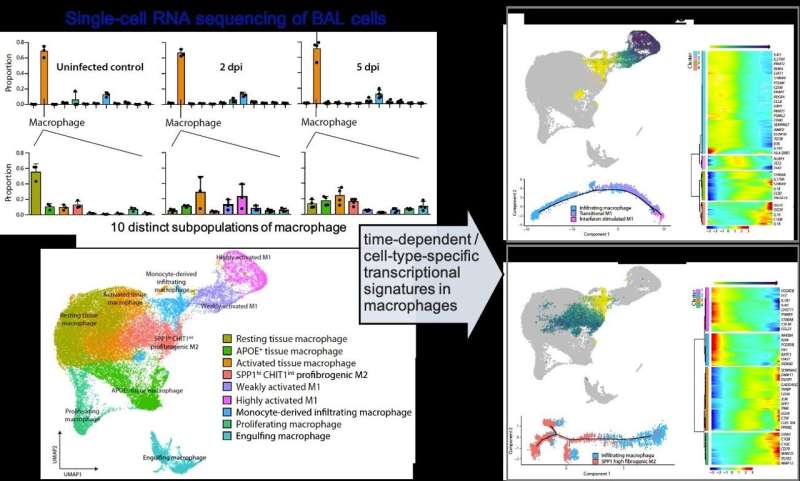
A KAIST immunology research team found that a specific subtype of macrophages that originated from blood monocytes plays a key role in the hyper-inflammatory response in SARS-CoV-2 infected lungs, by performing single-cell RNA sequencing of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid cells. This study provides new insights for understanding dynamic changes in immune responses to COVID-19.
In the early phase of COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2 infected lung tissue and the immediate defense system is activated. This early and fast response is called ‘innate immunity,” provided by immune cells residing in lungs. Macrophages are major cell types of the innate immune system of the lungs, and newly differentiated macrophages originating from the bloodstream also contribute to early defenses against viruses.
Professor Su-Hyung Park and his collaborators investigated the quantitative and qualitative evaluation of immune responses in the lungs of SARS-CoV-2 infected ferrets. To overcome the limitations of research using patient-originated specimens, the researchers used a ferret infection model to obtain SARS-CoV-2 infected lungs sequentially with a defined time interval.
The researchers analyzed the 10 subtypes of macrophages during the five-day course of SARS-CoV-2 infection, and found that infiltrating macrophages originating from activated monocytes in the blood were key players for viral clearance as well as damaged lung tissue. Moreover, they found that the differentiation process of these inflammatory macrophages resembled the immune responses in the lung tissue of severe COVID-19 patients.
Currently, the research team is conducting a follow-up study to identify the dynamic changes in immune responses during the use of immunosuppressive agents to control hyper-inflammatory response called ‘cytokine storm’ in patients with COVID-19.
Dr. Jeong Seok Lee, the chief medical officer at Genome Insight Inc., explained, “Our analysis will enhance the understanding of the early features of COVID-19 immunity and provide a scientific background for the more precise use of immunosuppressive agents targeting specific macrophage subtypes.”
Source: Read Full Article


