Sexually dimorphic placental antibody transfer during SARS-CoV-2 infection
Sex-based differences in COVID-19 disease transmission, severity, and mortality have been reported since the early stages of the pandemic in infants, with the underlying mechanism accounting for these differences not yet fully understood.
In a paper recently published in the journal Science Translational Medicine by Bordt et al. (October 19th, 2021), maternal SARS-CoV-2 infections are studied with particular regard to maternal-fetal antibody transfer and virus-induced placental interferon responses, finding a sexually dimorphic response that results in lesser antibody transfer to the male fetus.
A higher rate of severe SARS-CoV-2 has been reported amongst male than female infants, also more commonly manifesting as multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C). Newborn immunity is heavily dependent on the transfer of maternal immunoglobulin-G (IgG) via the placenta. This process is currently exploited in generating vaccine-induced immunity within the fetus against viruses such as influenza.
Maternal IgG is transferred to the fetus by neonatal Fc receptors in the placenta, of which there are several types (FcRn, FCγRII, and FCγRIII), and the expression of which is modulated by type I and II interferon. Sex-based differences in interferon signaling response to SARS-CoV-2 have been noted in the adult population, though few studies have focused on the more exaggerated difference noted in infants.
How was the study performed?
Sixty-eight pregnant women diagnosed with or at risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection were recruited for the study, with cases confirmed by RT-PCR testing. Blood samples were collected prior to birth and from the umbilical cord immediately after delivery, with further tissue biopsies also collected from the cord at this time. Half of the participants were bearing male or female children, respectively, with other demographics such as age and SARS-CoV-2 comorbidity risk equal between groups. Within this small sample size, no fetal differences in gestation age or disease severity were noted based on sex. However, overall, children of mothers infected with SARS-CoV-2 were on average of slightly lower birth weight. In addition, none of the infants born of previously SARS-CoV-2 infected mothers were themselves infected with the virus upon birth.
SARS-CoV-2 specific antibodies against the spike protein, receptor binding domain, S1 and S2 subunits of the spike protein, and nucleocapsid were characterized in each sample by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The group found that maternal IgG titers against SARS-CoV-2 antigens were lower in mothers carrying male fetuses than females. Further, that the titer of antibodies was lower in the umbilical cord relative to the mother's own titers when carrying a male infant. In female fetuses’ umbilical cords, a relative reduction in nucleocapsid specific cord IgG only was observed, with titers against the spike and its sub-regions maintained at the same level as in non-infected mothers. The group notes that IgG levels are lower amongst both female and male infants than expected based on observations of other pathogens such as influenza.dd
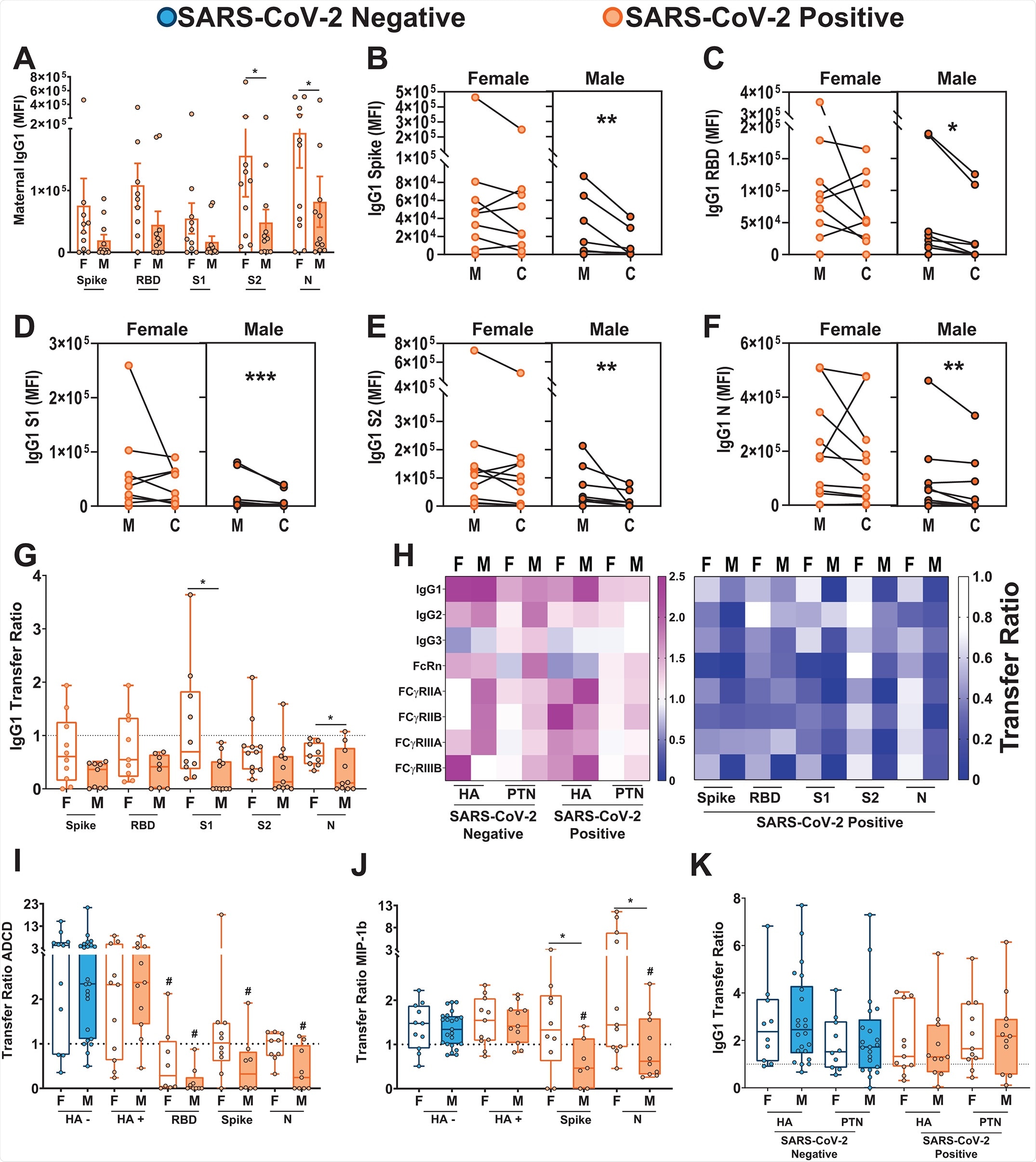
The group next compared the expression of Fc receptors in the placenta, finding increased expression in the placenta of male-bearing women compared to those carrying a female. This was associated with upregulation of FCGRT, FCGR1, and FCGR3A/B genes, accompanied by a proportional increase in FcRn, FCγRII and FCγRIII protein expression. Besides receptor quantity, it has also been found that Fc receptor co-localization is associated with placental antibody transfer, and the group observed that FCγRIII and FcRn were significantly more co-localized in male placentas.
Antibody glycosylation is known to be a factor in the transfer of antibodies across the placenta, and thus the group next examined the glycosylation of spike protein-specific antibodies in each participant. It was found that SARS-CoV-2 infected mothers produced spike-protein specific antibodies with markedly different glycan profiles than the non-infected, regardless of the sex of the fetus. The glycans demonstrated enhanced fucosylation, the addition of fucose residues, and prior studies have demonstrated that antibodies lacking fucosylation are better transferred by FCγRIII (Ferrara et al., 2011). Therefore, the enhanced expression and co-localization of FCγRIII in the male placenta could not overcome the reduced antibody-receptor affinity associated with fucosylation.
The expression of interferon stimulating genes was also found to be most aberrant in male SARS-CoV-2 exposed placentas, with a number of pro-inflammatory cytokines up or downregulated compared to female placentas. Anti-inflammatory factor interleukin-10, in particular, was upregulated in male placentas, while pro-inflammatory cytokines interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor were unaltered by SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Conclusions
The expected ratio of cord: maternal antibodies is around 1.1-1.5 during influenza infections, though it was found to be lower during SARS-CoV-2 infection. Newly born female babies to mothers previously infected with SARS-CoV-2 had a ratio of 0.85, dropping to 0.5 for males due to the impaired transfer of antibodies observed in this study. In both males and females, high placental expression of FCγRIII was associated with the lower transfer of subunit-1 spike protein-specific antibodies. However, high interleukin-10 expression was associated with the higher transfer in females only. Similarly, high expression of OAS1 was associated with higher antibody titers in males but not females. Disease severity and time since infection were discounted as factors in any observed difference, with no associations made.
- Bordt EA, Shook LL, Atyeo C, Pullen KM, De Guzman RM, Meinsohn MC, Chauvin M, Fischinger S, Yockey LJ, James K, Lima R, Yonker LM, Fasano A, Brigida S, Bebell LM, Roberts DJ, Pépin D, Huh JR, Bilbo SD, Li JZ, Kaimal A, Schust D, Gray KJ, Lauffenburger D, Alter G, Edlow AG. Maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection elicits sexually dimorphic placental immune responses. Sci Transl Med. 2021 Oct 19:eabi7428. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abi7428. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 34664987.https://www.science.org/doi/pdf/10.1126/scitranslmed.abi7428
Posted in: Child Health News | Medical Research News | Women's Health News | Disease/Infection News
Tags: Antibodies, Antibody, Antigen, Anti-Inflammatory, Assay, Birth Weight, Blood, Children, Coronavirus Disease COVID-19, Cytokines, Enzyme, Fc receptor, FcRn, Fluorescence, Genes, Glycan, Glycans, Glycosylation, immunity, Immunoglobulin, Influenza, Interferon, Interleukin, Interleukin-6, Macrophage, Medicine, Mortality, Necrosis, Newborn, Pandemic, Placenta, Protein, Protein Expression, Receptor, SARS, SARS-CoV-2, Spike Protein, Syndrome, Tumor, Tumor Necrosis Factor, Umbilical Cord, Vaccine, Virus

Written by
Michael Greenwood
Michael graduated from Manchester Metropolitan University with a B.Sc. in Chemistry in 2014, where he majored in organic, inorganic, physical and analytical chemistry. He is currently completing a Ph.D. on the design and production of gold nanoparticles able to act as multimodal anticancer agents, being both drug delivery platforms and radiation dose enhancers.
Source: Read Full Article


